User Research for a Language-Learning App
Title: Designing an Immersive and Personalized Language-Learning App
Role: User research, competitor analysis, persona creation, and empathy mapping
Timeline: One week
Skills & Tools Covered: User Research, User Persona, Empathy Mapping, Survey, Primary Research, Secondary Research, Competitor Analysis
Objective
To create a language-learning app that addresses diverse user needs by offering tailored, interactive, and culturally immersive learning experiences.
Problem Statement
Language learners face challenges such as staying motivated, finding time, lack of social interaction, and accessing tailored resources. A user-centered app with interactive and flexible content is needed to support diverse age groups and learning preferences.
Research Goal
I want to understand the processes and emotions that people experience around language learning applications.
I want to identify common user behaviors and experiences with tasks that my product is trying to address.
I want to understand user needs and frustrations related to the Language-Learning App.
Research Methods
I created questions for the survey and a Google survey form. I surveyed ten users aged 5–70 to understand their language-learning preferences, challenges, and habits.
Research Journey
To design a language-learning app that offers an immersive and personalized experience, I began by empathizing with potential users' needs, motivations, and frustrations. My research included an online survey targeting users aged 5-70 with a diverse demographic range. The survey helped me understand their learning habits, challenges, and preferred methods. Additionally, I conducted competitor analysis on popular apps like Duolingo, Babbel, and Busuu to identify successful features and gaps in the market. Throughout this journey, I focused on understanding the emotional and practical aspects of language learning, collecting insights about user engagement, pain points, and the importance of social and interactive elements in the learning process.
Regarding demographics, the age distribution shows that most respondents (66.7%) are between the ages of 31 and 50, suggesting that adults in this age range are particularly motivated to learn languages. Additionally, 33.3% of respondents are under 18, which might reflect an educational requirement or early interest in languages.
50% of respondents were Male, and 50% were Female.
90% of respondents were from USA and 10% respondents were from India.
60% of respondents were graduates, 20% had less than a high school degree, 10% had a high school degree or equivalent, and 10% had a bachelor's degree.
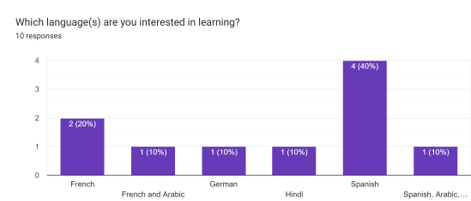
25% of people were learning French, 10% were learning Arabic, 10% were learning German, 10% were learning Hindi, and 45% were learning Spanish.
70% of respondents are beginners, and 30% are intermediate in the language they are learning. Since users have different language knowledge levels, it is important to add content depending on their level.
The survey data reveals interesting trends regarding the motivations of language learners. Most respondents are learning new languages out of personal interest (70%) and for travel purposes (50%), highlighting the value of languages beyond academic or career-based reasons. While only 10% of respondents are driven by career advancement, this underscores the growing importance of language skills in personal and cultural contexts.
70% of respondents were employed, 20% were students, and 10% were unemployed. People in different life stages and career situations like to learn new languages, so the app should be adaptable to that.
50% of responders learn language daily, 30% learn weekly, and 20% learn only occasionally. People from different learning frequencies like to learn new languages, so the app should provide flexible lesson plans, daily and weekly engagement options, and progress-tracking tools for each type of learner.
70% of respondents like to learn through interactive exercises, 60% responded through listening to audio, 50 % through conversation, 30% through reading and writing, and 10% through watching videos.
Since most users favor learning through interactive exercises, the app should prioritize engaging and hands-on activities like quizzes, flashcards, and word-matching games. This interactive format keeps learners actively involved and reinforces their learning.
A significant portion of users prefer audio learning. Offering audio lessons, such as background learning while commuting or exercising, will help these users and benefit time-constrained learners.
50% of users like conversation-based learning, which allows them to practice speaking in real-life scenarios.
Learning through watching videos is the least preferred method, but it can still be helpful for visual learners. Including short, engaging videos with practical demonstrations of language use benefits the users.
70% of respondents face the challenge of staying motivated, 60% need more practice opportunities, 40% have less time, and 20% find it challenging to understand the grammar.
Since most learners struggle to remain motivated, the app must integrate features encouraging sustained engagement.
The lack of real-world practice was a significant issue for 60% of users. The app should emphasize conversational practice through chatbots, live speaking sessions, and connecting learners with native speakers.
Users find it challenging to allocate time for learning. Flexible learning options like short lessons, audio lessons for passive learning, and offline capabilities can help accommodate busy schedules.
20% found grammar a significant issue; providing interactive grammar games and real-world examples can also address this challenge without overwhelming the user.
50% of respondents like interactive exercises feature, process tracking goal setting, and one-to-one tutoring, 40% prefer pronunciation practice, and 30% prefer offline lessons.
Half of the respondents want engaging exercises that track their progress. They need an adaptive learning path where users can set goals and see measurable progress. Including one-on-one tutoring as a feature would help learners receive personalized guidance and enhance their learning experience.
Half of the users expressed interest in pronunciation-focused exercises.
A third of users prioritize the ability to learn without an internet connection, reinforcing the importance of downloadable content and offline capabilities. This feature ensures that users can continue learning even in areas with limited connectivity.
According to the survey data, 70% of respondents were using mobile devices for language learning, while 30% were using desktop or laptop computers. This suggests a strong preference for mobile learning, indicating that the app’s design and features should prioritize mobile usability. This aligns with the need for:
A good, responsive mobile interface.
Features optimized for smaller screens include simple navigation, touch-friendly controls, and minimal text input requirements.
Using mobile capabilities like notifications and background audio for passive learning opportunities.
Given that mobile devices offer portability, voice recognition, and background learning options.
Most participants suggested having a feature to connect with people to study together and have conversations. Some others suggested having a learning game feature, a friendly user interface, encouraging reading and writing and pointing out the corrections, and background learning to learn while doing other works.
Insights
1. Target Audience:
Mid-career adults: Language learning for personal and professional growth, driven by the desire to stay globally connected. They prefer flexible and work-life balance-friendly options.
Under-18 learners: Their language learning is typically academic, so gamified and immersive formats could enhance their engagement.
2. Content Structure and Personalization:
Knowledge levels: Content must be tailored to various proficiency levels (beginner, intermediate, advanced). Personalized learning paths will help.
Learning frequency: Users have different preferences (daily or weekly). The platform should offer flexibility and progress tracking.
3. Learning Methods:
Interactive learning: Hands-on activities (quizzes, flashcards, word-matching games) are essential. Conversation-based learning provides practical language practice.
Grammar focus: Gamified grammar exercises and real-world examples can help without overwhelming learners.
4. Flexibility:
Time constraints: Audio lessons, short bursts of learning, and offline learning (e.g., during commutes or exercising) will appeal to time-constrained users.
5. Motivation:
Features that sustain engagement, such as gamification, social features (studying together, having conversations), and adaptive learning paths, are crucial.
6. Technology:
Mobile learning: Users strongly prefer mobile platforms for learning due to portability and background learning features.
Progress tracking: Learners need tools that track progress and provide adaptive feedback.
7. Community:
Social learning: A feature allowing learners to connect with peers for study sessions or conversations will enhance the learning experience.
8. Tutor Integration:
One-on-one tutoring: Personalized guidance through tutoring options could further enrich user engagement and learning outcomes.
9. Additional Features:
User-friendly interface: It is vital to have a simple and intuitive interface that supports multiple forms of engagement (reading, writing, corrections).
Background learning: Learners would benefit from passive learning opportunities, like listening while doing other tasks.
Competitive Research
Duolingo stands out for its gamified learning approach, which encourages consistent practice through engaging activities like earning XP points, leveling up, and tracking progress. It has simplicity, ease of use, and the ability to fit language learning into a user's daily routine. With over 40 languages and interactive short stories, Duolingo targets users looking for a fun, interactive learning experience. It enjoys a monthly traffic of 5.1 million and benefits from organic growth, mainly through YouTube, with no paid traffic. However, its focus is on short lessons, which helps busy users.
Babble is tailored for users seeking structured, real-life conversational skills. It provides a more comprehensive learning experience, covering speaking, writing, listening, and grammar in short lessons that fit busy schedules. Babble excels in offering specialized courses for specific goals, like business language and travel phrases. With 14 languages and a monthly traffic of 1.4 million, it attracts a more professional or goal-oriented audience. However, Babble relies more heavily on paid traffic (221 visitors), which may limit organic reach. Most of its inbound links come from Apple.com.
Busuu offers a blend of structure and personalization, focusing on real-world language practice. Its personalized study plans and offline lesson availability make it ideal for users who want to learn at their own pace and offline. Busuu supports 14 languages. Its monthly traffic of 12.4 million makes it the most visited platform among the three, with some reliance on paid traffic (3,072). It also enjoys referrals from Apple.com, indicating strong brand visibility. Busuu's structured approach is complemented by its community-based learning, allowing users to interact with native speakers.
Personas
Empathy Map
Learnings
The research revealed key insights that will shape the app design. Users value flexible, mobile-friendly platforms with personalized learning paths that adapt to their proficiency levels and schedules. Gamified elements, interactive exercises, and social features, such as studying with peers or practicing conversations, are essential for sustaining motivation, especially for beginners. Additionally, users appreciate tools for progress tracking, grammar-focused activities, and cultural immersion. For time-constrained learners, features like offline access and passive learning options, such as audio lessons during commutes, are vital. By addressing these needs and challenges, the app can provide a seamless, engaging, and effective learning experience for a wide range of users.
Challenges
Balancing diverse user needs across age groups.
Deep understanding of user-centered design principles and the power of empathy in UX.